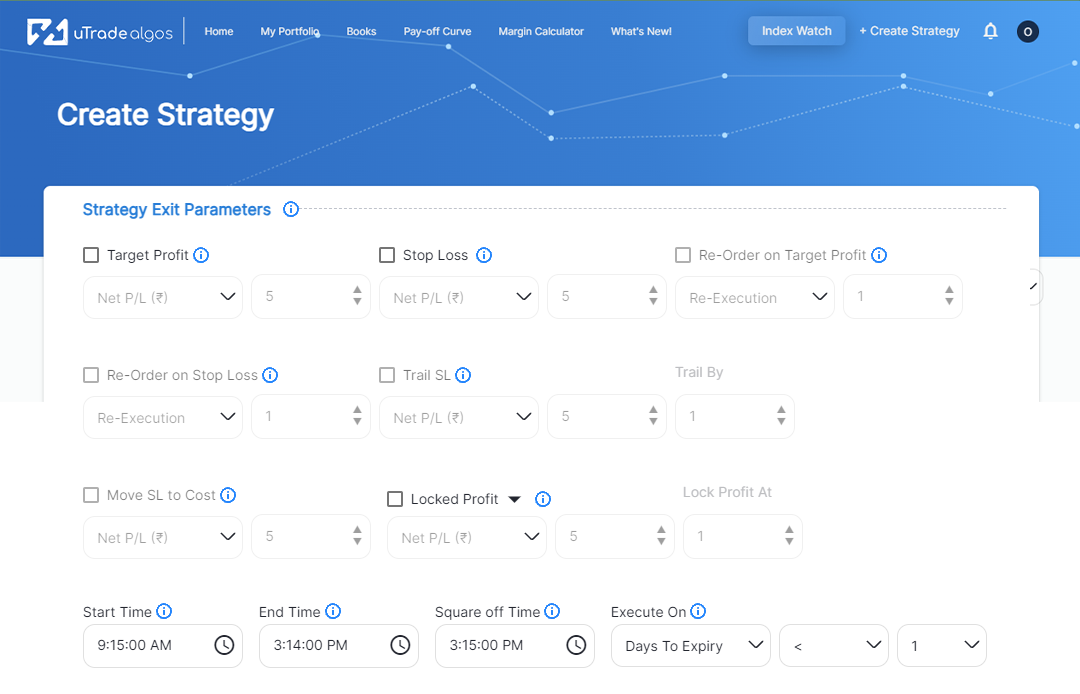
Trading in financial markets, whether stocks, commodities, or currencies, is a challenging endeavour. It requires a thorough understanding of market dynamics, effective strategies, and the ability to adapt to changing conditions. To increase the chances of success, traders often use backtesting and forward testing. These techniques help evaluate the performance of trading strategies and determine their viability in real-world scenarios. Here, we will find out what backtesting and forward testing are, their importance, and how they can be used effectively in trading strategies.
Backtesting
What Is Backtesting?
Backtesting is a crucial component of trading strategy development. It involves applying a trading strategy to historical market data to assess how it would have performed had it been applied in the past. Essentially, it is a simulation of trading on backtesting platforms that allows traders to analyse how a strategy would have fared under various market conditions.
Why Is Backtesting Important?
- Strategy Validation: Backtesting helps validate trading strategies. It allows traders to see how their strategies would have performed historically, providing a degree of confidence in their viability.
- Risk Assessment: By analysing historical performance, traders can gain insights into the potential drawdowns, losses, and other risks associated with their strategy. Online algo platforms like uTrade Algos help with algo backtest through the use of accurate historical data. This results in comprehensive risk assessment reports.
- Parameter Optimisation: Backtesting enables traders to fine-tune strategy parameters. It allows for the adjustment of variables to improve strategy performance.
How to Perform Backtesting
- Data Collection: The first step in backtesting is acquiring historical data for the asset or market you plan to trade. High-quality data sources, such as those available with uTrade Algos’ backtesting, are essential for accurate results.
- Strategy Implementation: Code or define the trading strategy in a way that can be applied to historical data. This could be done using specialised algo backtest software or programming languages like Python or R.
- Testing: Apply the strategy to historical data, accounting for transaction costs, slippage, and other trading expenses that would occur in real life.
- Analysis: Evaluate the results, considering metrics like profit and loss, drawdowns, risk-reward ratios, and other performance indicators.
- Refinement: If necessary, refine the strategy based on the results and run additional tests until satisfied with the performance.
Common Backtesting Pitfalls
- Overfitting: This occurs when a strategy is too closely tailored to historical data and performs poorly in real-time market conditions. To avoid this, use out-of-sample data for validation.
- Ignoring Transaction Costs: Neglecting to account for commissions, spreads, and slippage can lead to overly optimistic results that don’t reflect real-world trading.
- Lack of Realism: Ensure that the backtesting process mimics real trading conditions as closely as possible, including liquidity, order execution, and market hours.
Forward Testing
What Is Forward Testing?
While backtesting evaluates a strategy’s historical performance, forward testing is about assessing how a strategy performs in real-time, current market conditions. It is essentially a way to paper trade your strategy without committing real capital.
Why Is Forward Testing Important?
- Real-World Assessment: Forward testing allows traders to assess how a strategy performs under current market conditions, considering factors that may not be present in historical data.
- Adaptability: It helps traders identify if a strategy can adapt to changing market conditions. If a strategy works well historically but struggles in real-time, adjustments may be necessary.
- Psychological Preparation: It provides psychological preparation for live trading. Traders can become accustomed to the emotional aspects of executing their strategy.
How to Perform Forward Testing
- Paper Trading: Execute your strategy with virtual capital as if it were real trading. Many brokerage platforms offer paper trading accounts for this purpose.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuously monitor the performance of your strategy as it interacts with the live market. Keep detailed records of your trades.
- Analysis and Adjustment: Regularly review the results and adapt the strategy as necessary. Pay attention to metrics like win rate, profit and loss, and drawdowns.
Common Forward Testing Pitfalls
- Overconfidence: Traders may become overconfident after a series of successful paper trades, leading to poor decision-making when they start trading with real capital. To avoid this, treat paper trading as realistically as possible.
- Neglecting Emotions: Even though forward testing doesn’t involve real money, it’s important to consider the emotional aspects of trading. Recognise how you react to losses and gains and work on maintaining discipline.
- Insufficient Testing Period: It’s essential to forward test a strategy for an extended period to account for different market conditions. A few successful trades do not guarantee a strategy’s long-term viability.
In the world of trading, success is not guaranteed, but meticulous planning and testing can greatly improve your odds. Both backtesting and forward testing play critical roles in the development and validation of trading strategies. By incorporating both backtesting and forward testing into your trading strategy development process, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of how your strategies are likely to perform, ultimately increasing your chances of success in the complex world of financial markets.

 November 3, 2023
November 3, 2023